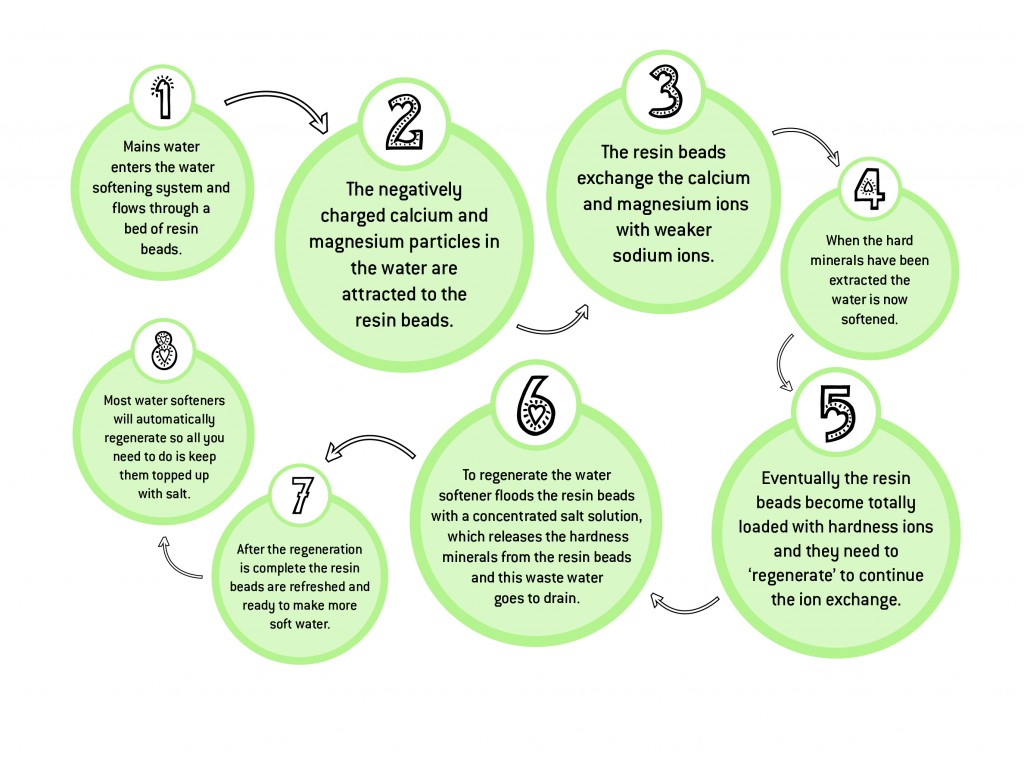
Eventually all of the resin exchange sites are occupied by calcium and magnesium and no further softening exchange can take place. The resin is said to be exhausted and must be regenerated.
The resin of the softener is regenerated with a brine solution. During regeneration the flow of service water from the softener is stopped.
Brine is drawn from the brine tank, mixing water with the salt in the reservoir. The brine solution flows through the resin, contacting the resin beads loaded with calcium and magnesium ions. Even though the calcium and magnesium are more strongly charged than the sodium, the concentrated brine solution contains literally billions of the more weakly charged sodium ions.
This way, the sodium ions have the power to displace the smaller number of calcium and magnesium ions. When the calcium and magnesium ions are displaced, the positive sodium ions are then attracted to the negatively charged exchange sites on the resin.
Eventually, all exchange sites are taken up by sodium ions. The resin is said to be regenerated and ready for the next softening cycle.
Want to know more about water softening? Book a free visit from one of our authorized dealers via the form below!